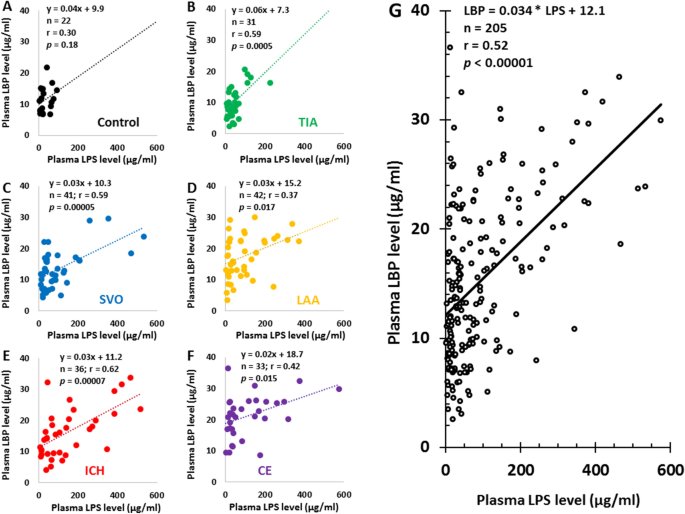
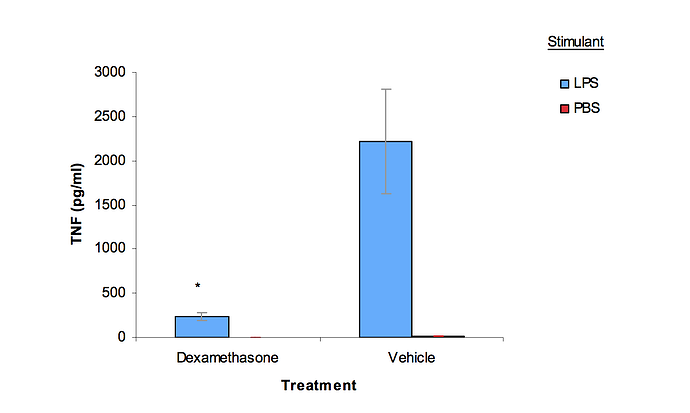
Lipopolysaccharide administration for a mouse model of cerebellar ataxia with neuroinflammation | Scientific Reports

Serum amyloid A promotes LPS clearance and suppresses LPS‐induced inflammation and tissue injury | EMBO reports
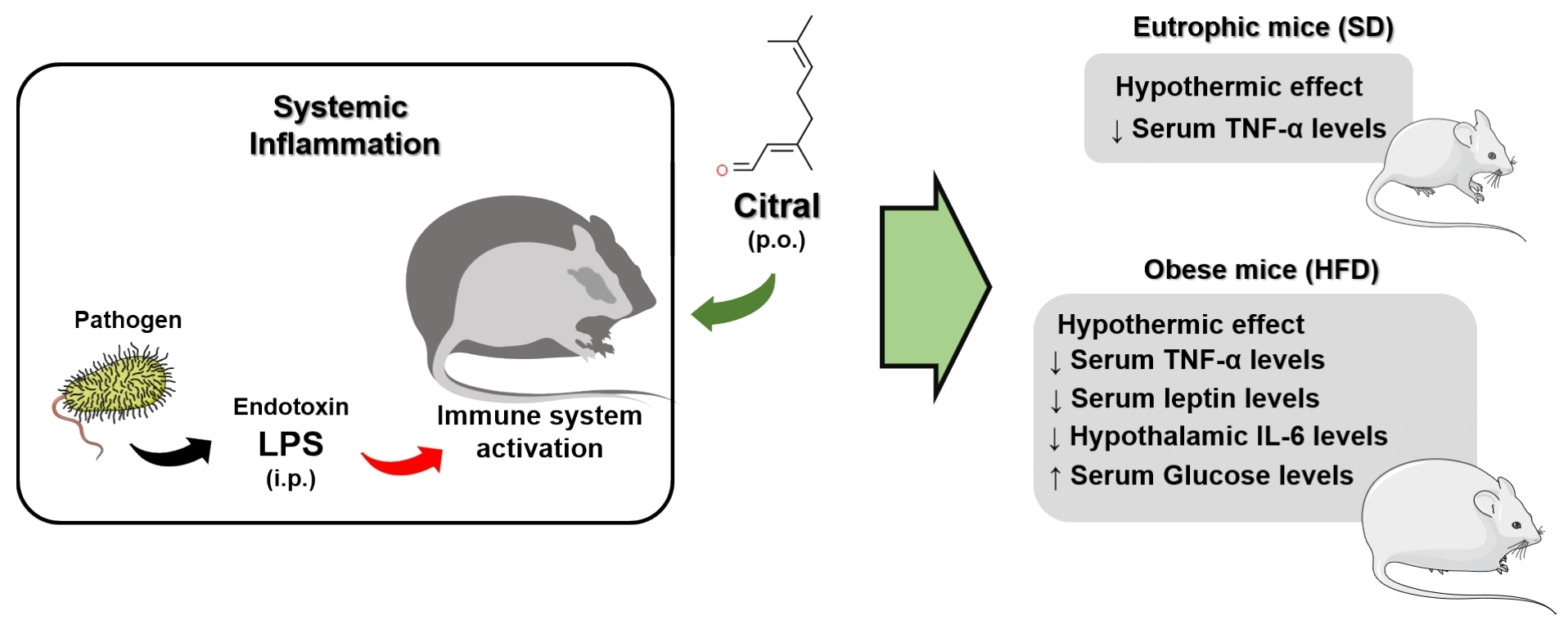
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | Hypothermic Effect of Acute Citral Treatment during LPS-induced Systemic Inflammation in Obese Mice: Reduction of Serum TNF-α and Leptin Levels
Oxypeucedanin relieves LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the inflammation and maintaining the integrity of the lung air-blood barrier | Aging
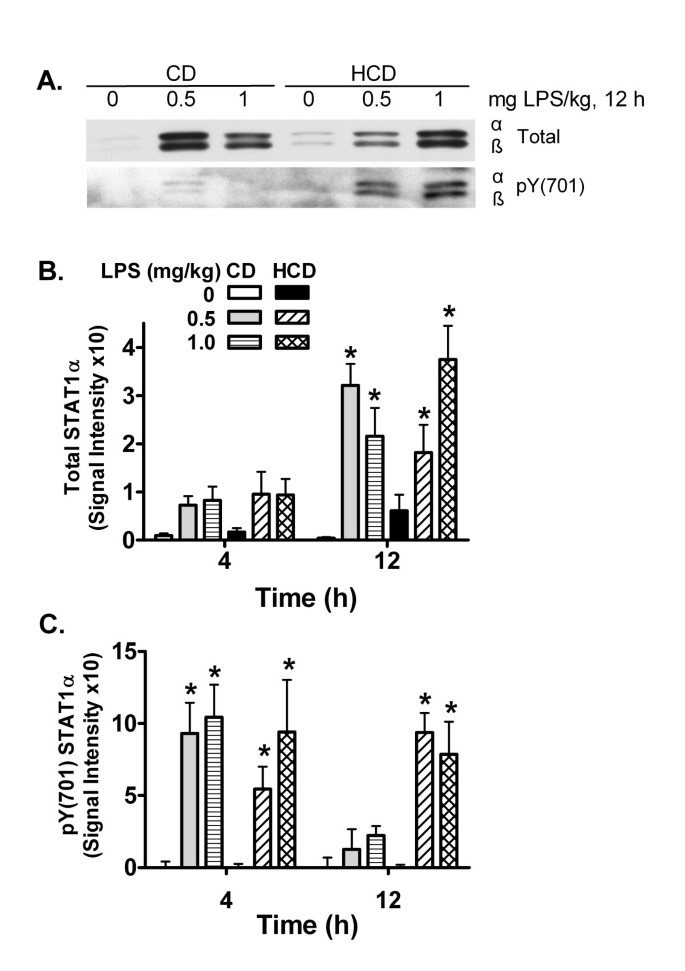
Sensitivity of mice to lipopolysaccharide is increased by a high saturated fat and cholesterol diet | Journal of Inflammation | Full Text
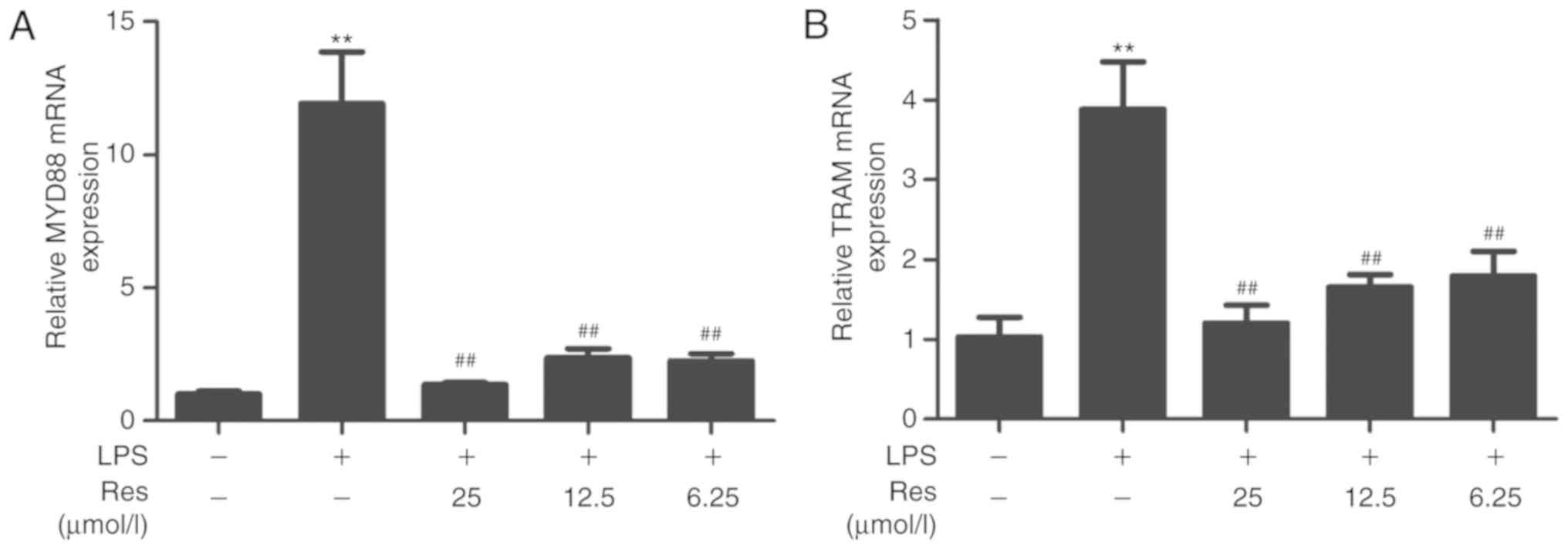
Resveratrol inhibits LPS‑induced inflammation through suppressing the signaling cascades of TLR4‑NF‑κB/MAPKs/IRF3

LPS-induced lung inflammation is linked to increased epithelial permeability: role of MLCK | European Respiratory Society
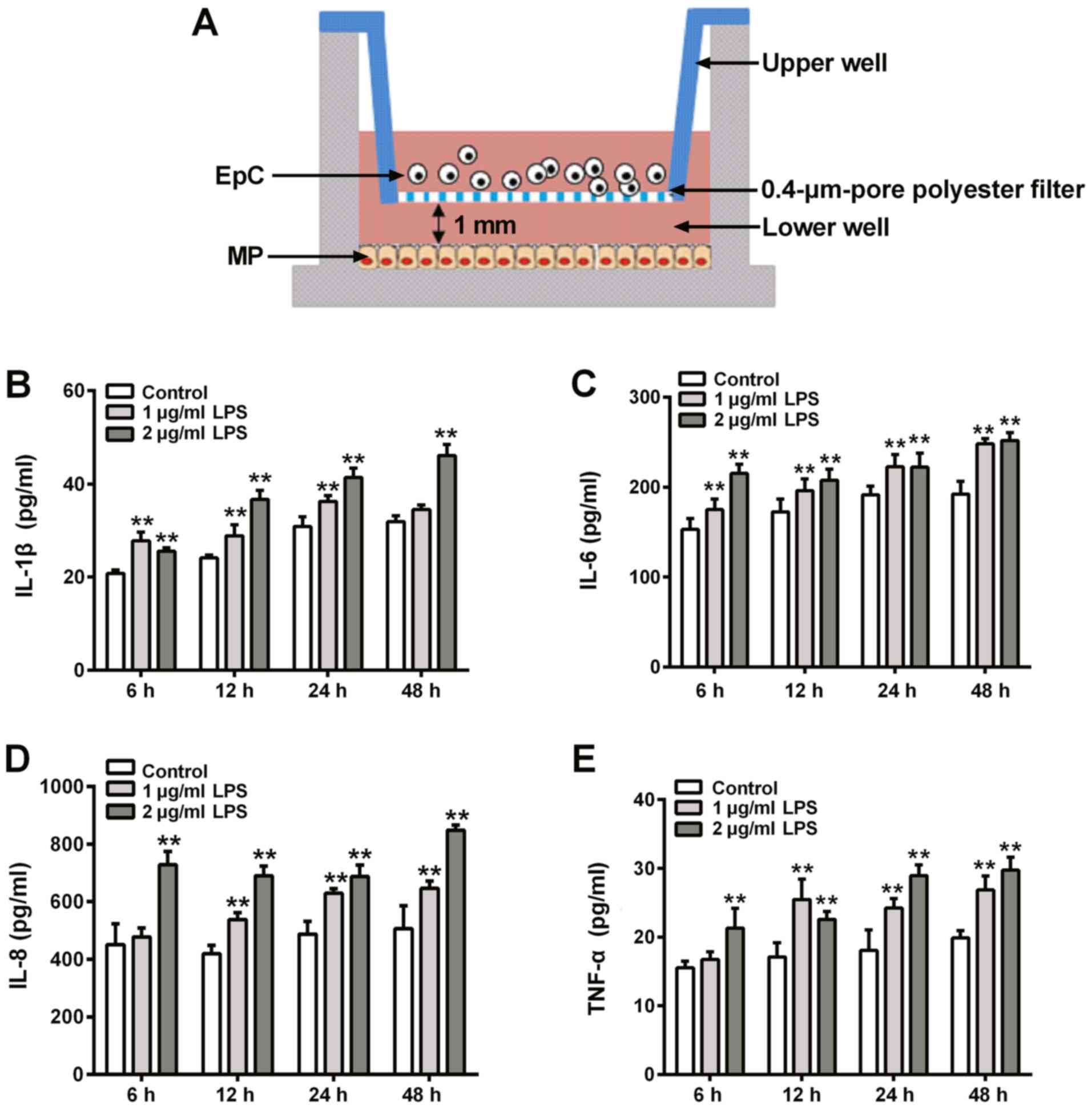
Mechanisms of the lipopolysaccharide‑induced inflammatory response in alveolar epithelial cell/macrophage co‑culture

Inhibition of Prostaglandin Synthesis Up-Regulates Cyclooxygenase-2 Induced by Lipopolysaccharide and Peroxisomal Proliferators | Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
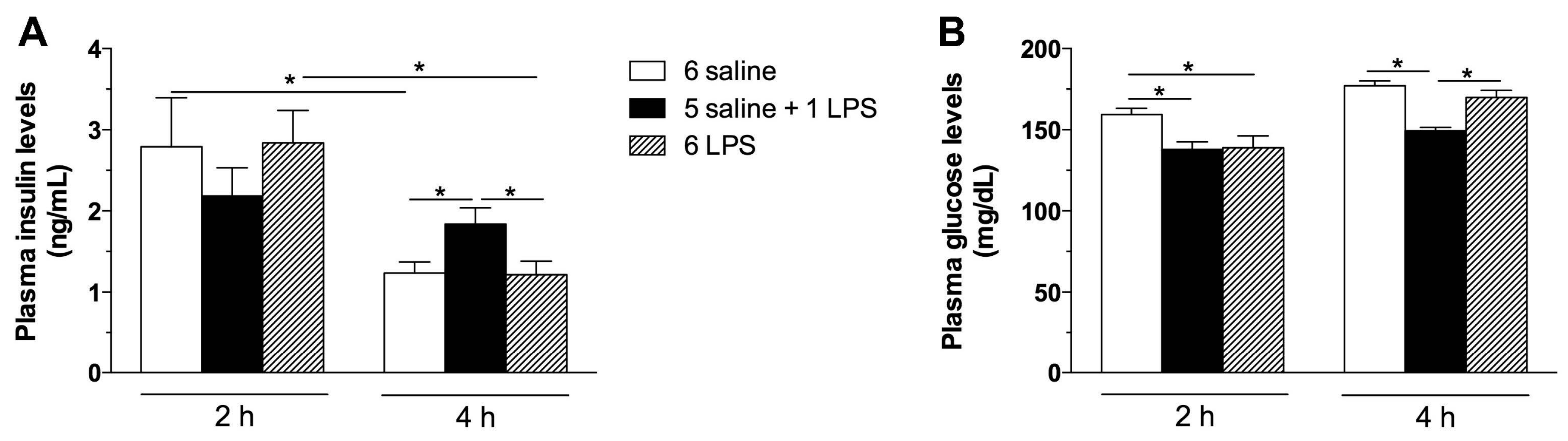
IJMS | Free Full-Text | LPS-Induced Low-Grade Inflammation Increases Hypothalamic JNK Expression and Causes Central Insulin Resistance Irrespective of Body Weight Changes

LPS induces rapid increase in GDF15 levels in mice, rats, and humans but is not required for anorexia in mice | American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology
LPS Exposure Increases Maternal Corticosterone Levels, Causes Placental Injury and Increases IL-1Β Levels in Adult Rat Offspring: Relevance to Autism | PLOS ONE

LDL-apheresis as an alternate method for plasma LPS purification in healthy volunteers, dyslipidemic and septic patients | medRxiv
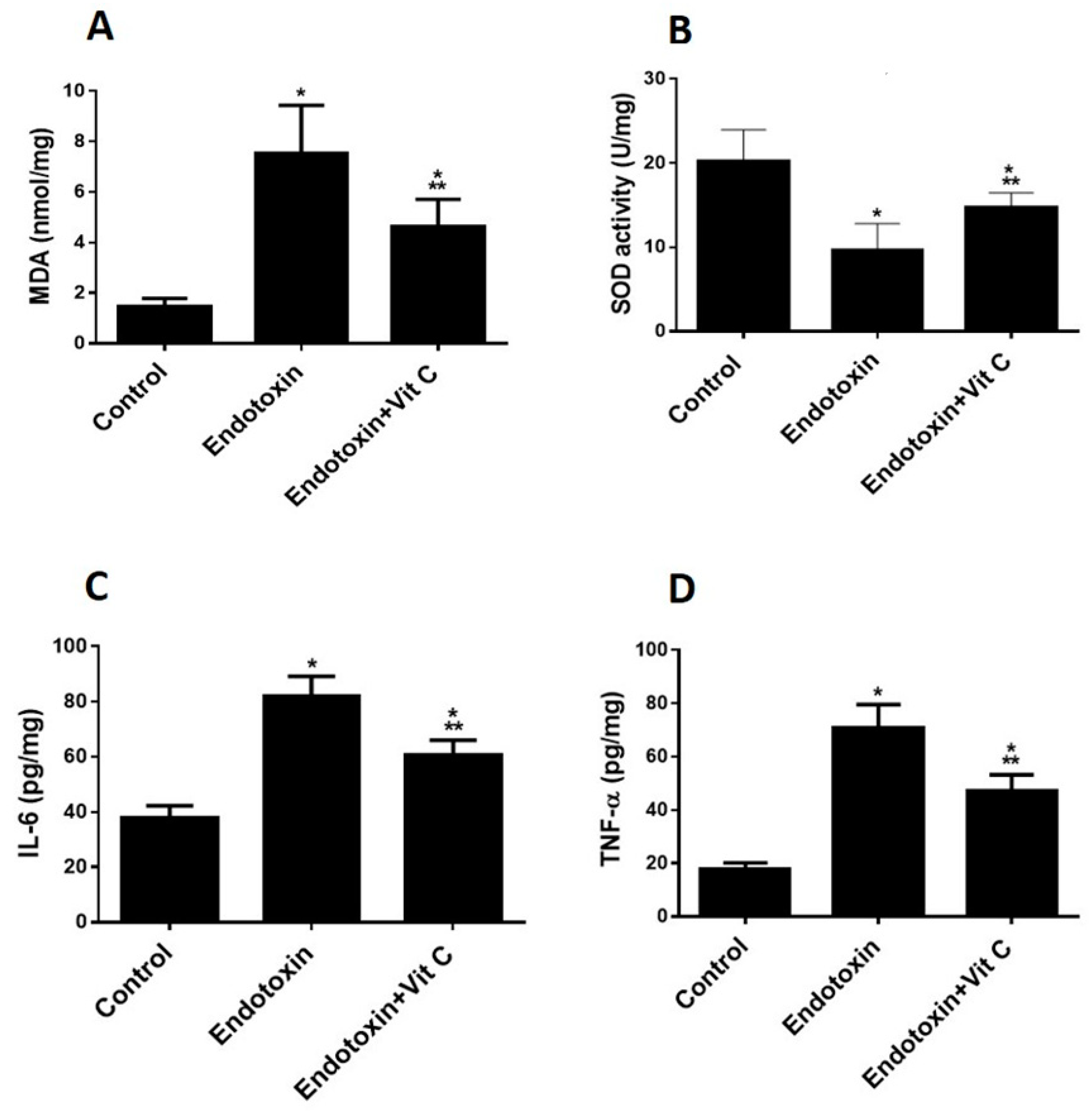
CIMB | Free Full-Text | Antioxidant Activity of Vitamin C against LPS-Induced Septic Cardiomyopathy by Down-Regulation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
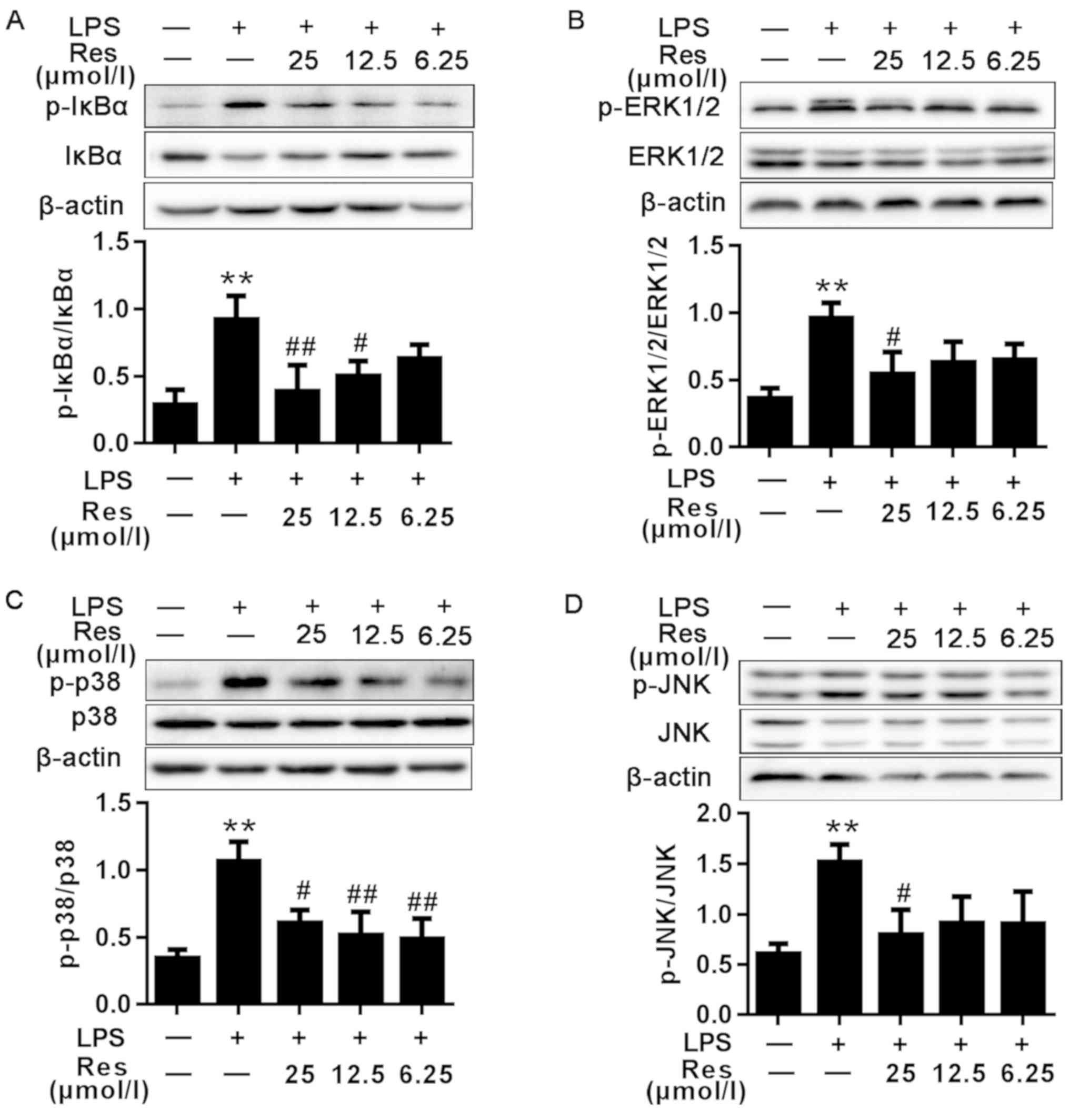
Resveratrol inhibits LPS‑induced inflammation through suppressing the signaling cascades of TLR4‑NF‑κB/MAPKs/IRF3
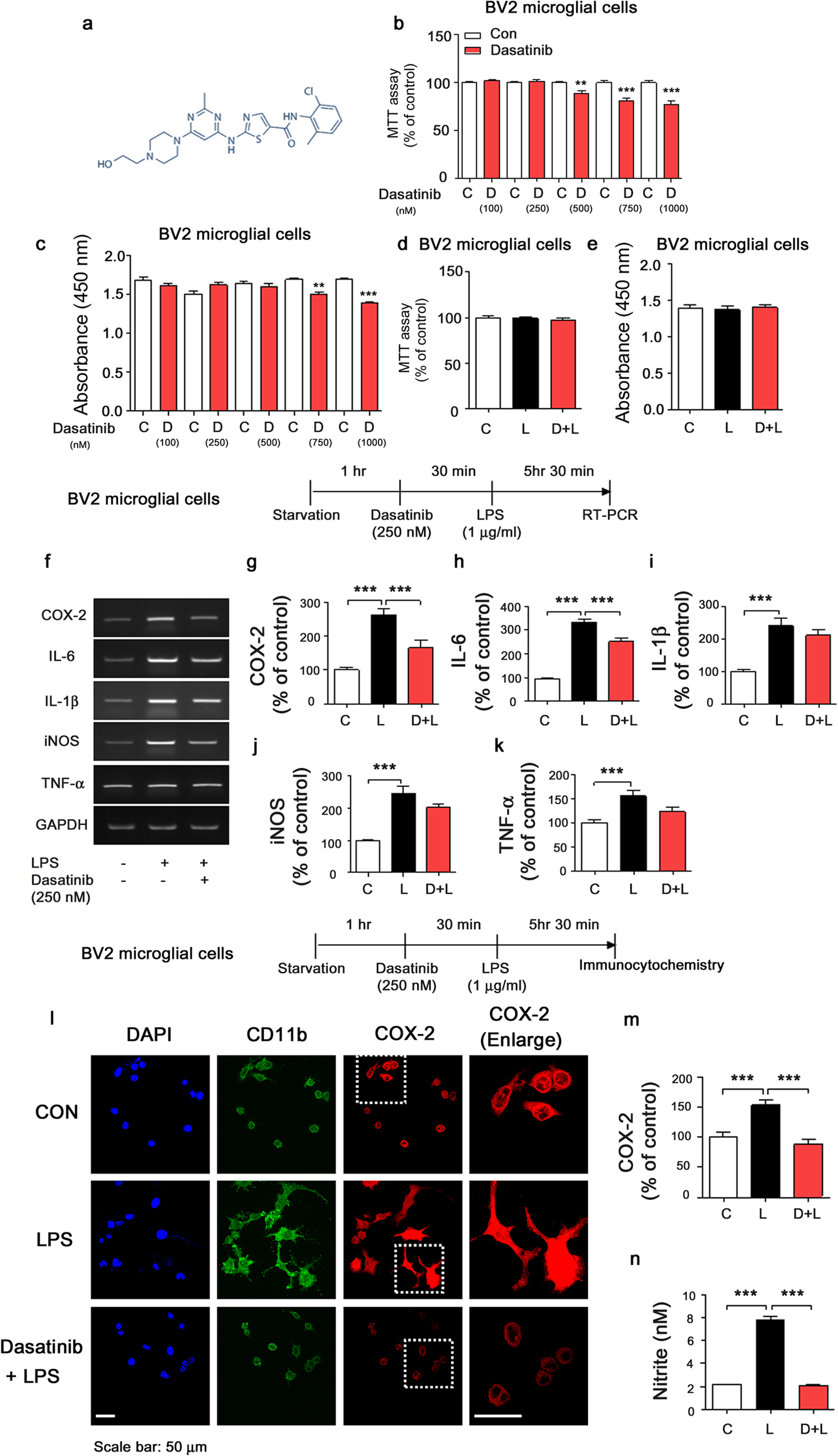
Dasatinib regulates LPS-induced microglial and astrocytic neuroinflammatory responses by inhibiting AKT/STAT3 signaling | Journal of Neuroinflammation | Full Text

Increased LPS levels coexist with systemic inflammation and result in monocyte activation in severe COVID-19 patients - ScienceDirect

Serum Levels of Lipopolysaccharide and 1,3-β-D-Glucan Refer to the Severity in Patients with Crohn's Disease

Increased levels of systemic LPS-positive bacterial extracellular vesicles in patients with intestinal barrier dysfunction | Gut