Prove that vectors a x (b x c) ≠ (a x b) x c if - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community

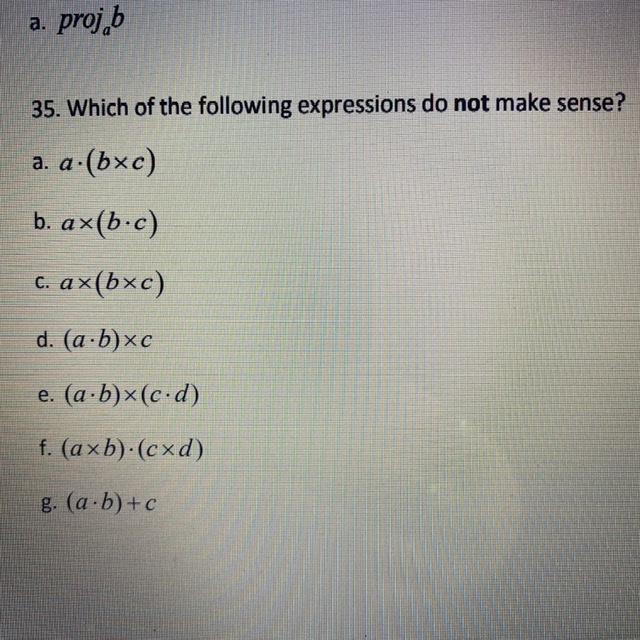
SOLVED: 2. If A, Band € are three vectors: Which of the following is not true? A(BxC) = scalar value Ax(BxC)= vector value Ax(B-C) = scalar value A(B+C) = scalar value

SOLVED: If a, b, and c are vectors and c is a scalar, then we have the following properties: 1.axb = -bXa 2. (ca) Xb = c(a X b) = aX (cb)

If vec a , vec b , vec c are unit vectors such that vec a + vec b + vec c = 0, then, vec a·vec b + vec b·vec c + vec c·vec a
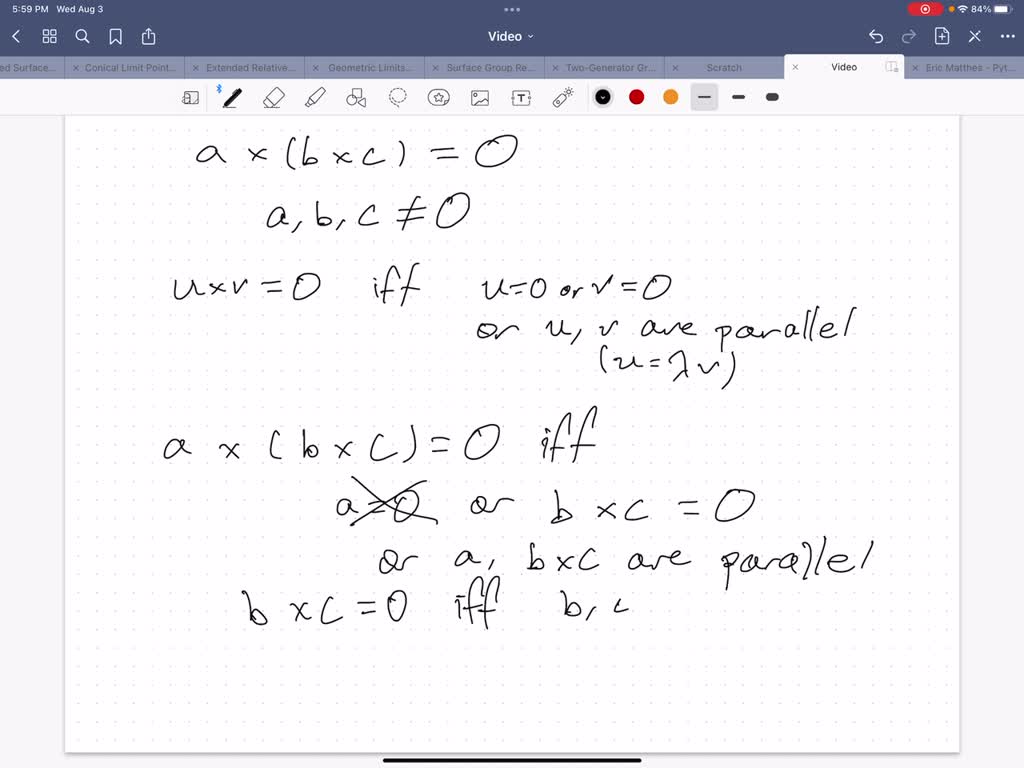
SOLVED: Choose the correct possibilities. If a x (b x c) = 0 and a, b and c are non-zero, vectors then A. b and c parallel to each other. B. b
Let x0 be the point of local maxima of f(x) = vector(a.(b x c)), where vector a = xi - 2j + 3k, vector b = -2i + xj - k and
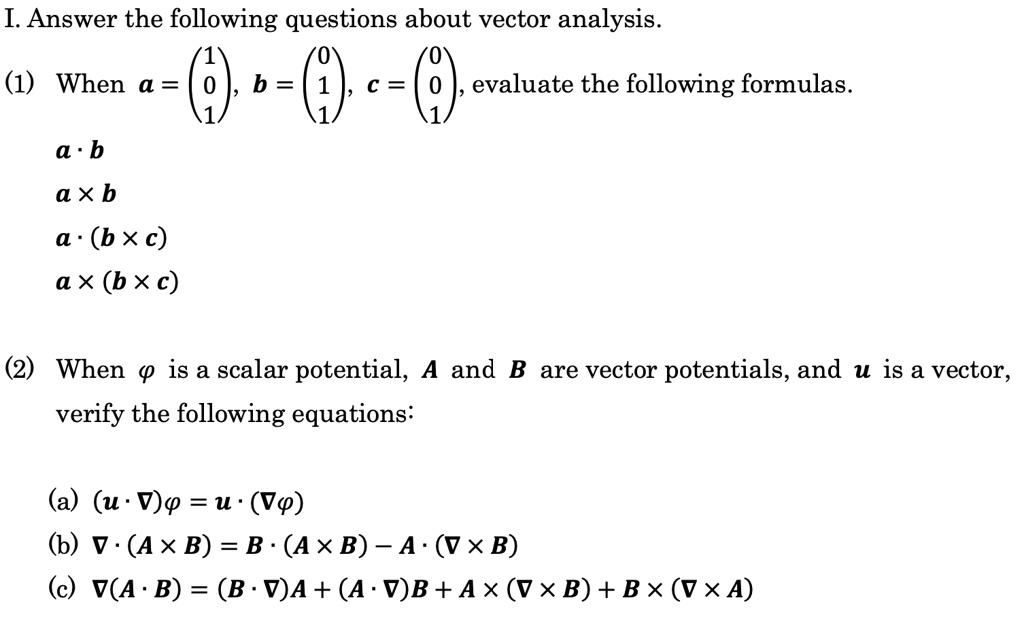
SOLVED: I Answer the following questions about vector analysis. (1) When a = b = c = evaluate the following formulas a . b aXb a . (bXc) ax (bxc) (2) When

SOLVED: Problem 1.2 Straight line connecting the tips of three vectors originating from point: Show that the tips of three vectors B, and € originating from common point lie along a straight

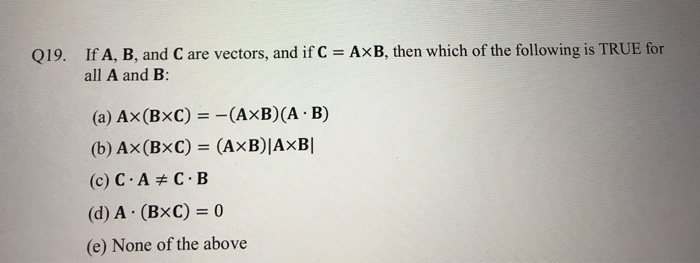


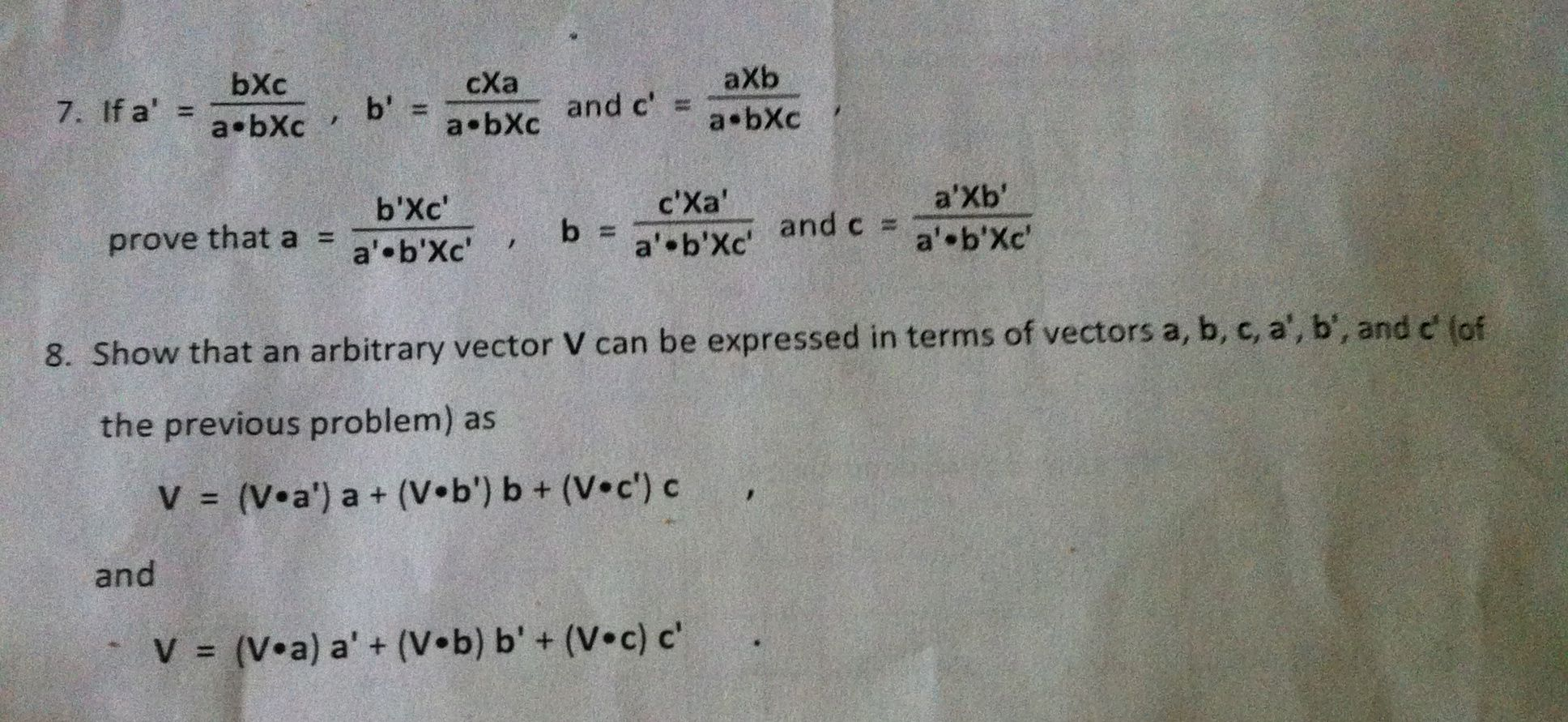
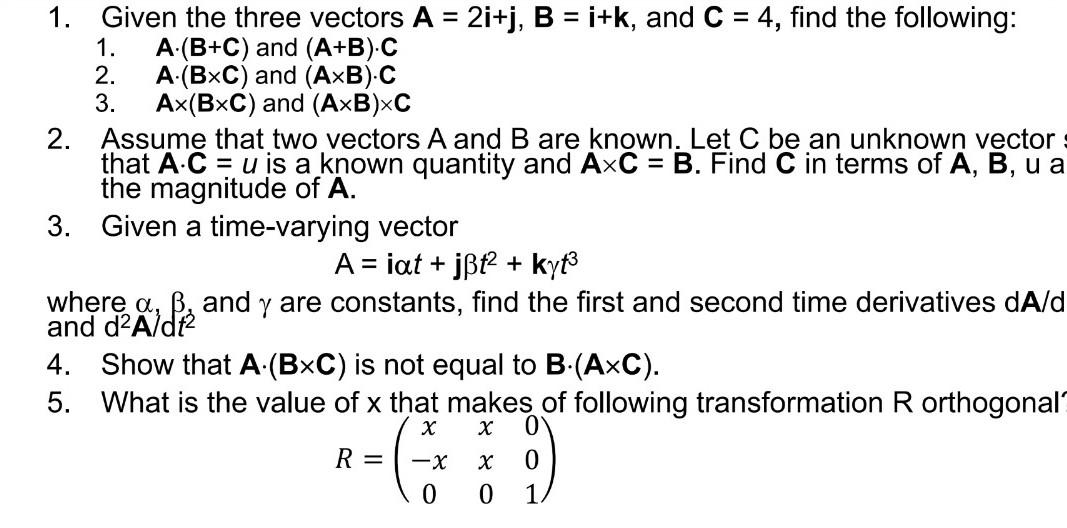
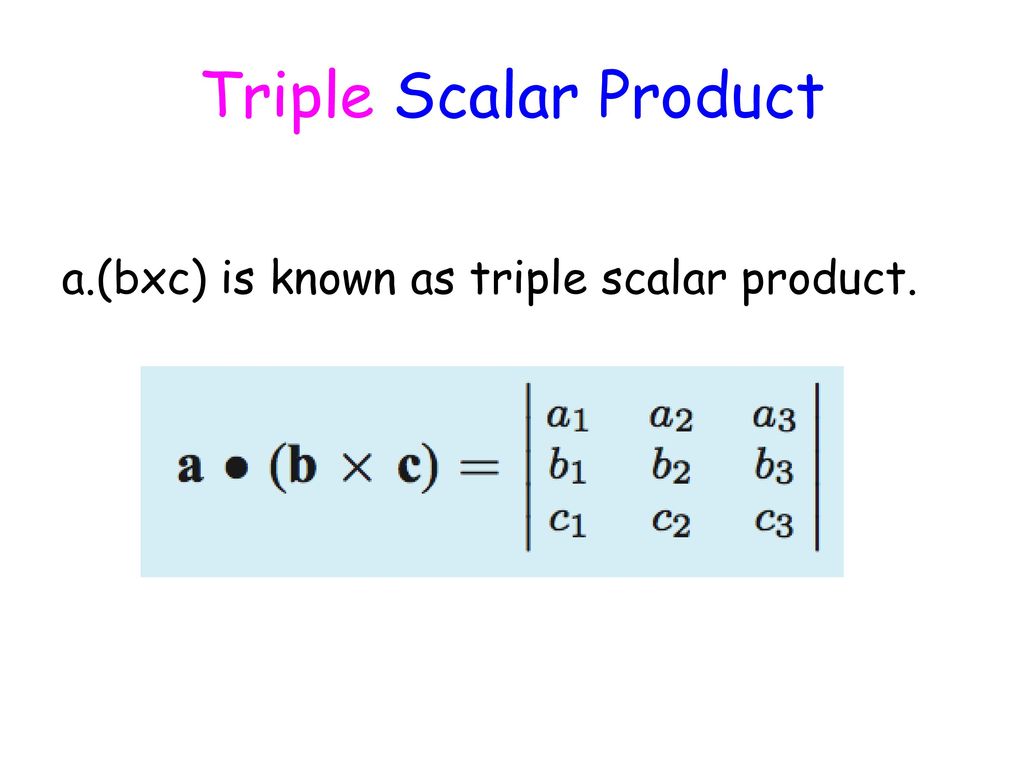
![What is the value of [axb bxc cxa] ? What is the value of [axb bxc cxa] ?](https://mypat-community-images-prod.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/web/5ace602f9fe7b01d581e2e4e1538651425478.Capture.PNG)



![Answered: If A = BxC, find matrix A. 2 1 1 -3 -2]… | bartleby Answered: If A = BxC, find matrix A. 2 1 1 -3 -2]… | bartleby](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/64b2dfc0-bcf1-429f-8331-3ea1dbd1cc71/ae89a7b1-49b4-49fa-a3ea-669c6192e123/8t756tb_processed.jpeg)