Differential Equations Linear. Separable y' = -2xy y'/y = -2x ln y = -x 2 + C y = e -x^2+c =C 1 e -x^2. - ppt download

calculus - The $y$-axis cuts the given family $y=cx^2$ orthogonally. But other option is correct (in GATE 2016). Why? - Mathematics Stack Exchange
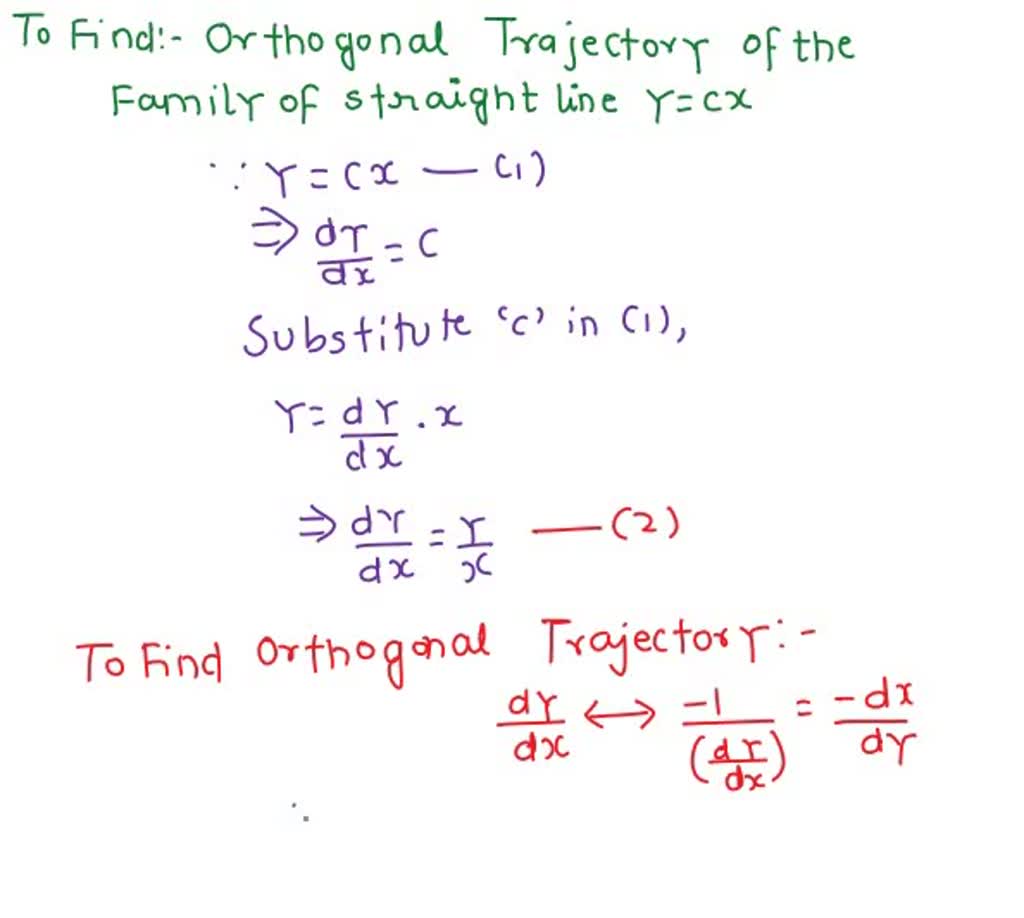
SOLVED: Find the orthogonal trajectories (OT) of the family of straight lines y = Cx. Describe the obtained family of curves/OT.

SOLVED: Differential Equations Bernoulli Equations Questions: Find the general solution of the equation y' y = y2ex y(C-x)zex, y-0 Solve the differential equation y' +> =y2 . yx(C-Inlxi)-1, y-0 Solve the equation

The orthogonal trajectories of the family of curves `y=Cx^(2)`, (C is an arbitrary constant), is - YouTube

SOLVED: Question One (1) Verify that a one-parameter family of solution for y = ry + (y)2 y = cx + . Determine a value of k such that y = kr
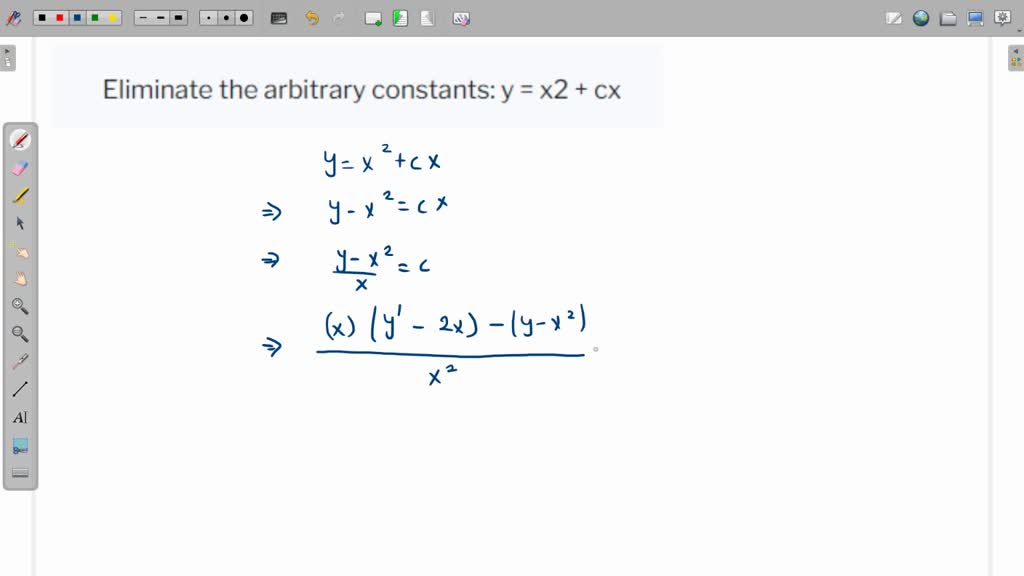
The equation y=cx^2 is the general solution of differential equation then what is the interval of the differential equation? - Quora

Let m and n be the order and the degree of the differential equation whose solution is, y = cx + c^2 - 3c^3/2 + 2 , where c is a parameter. Then
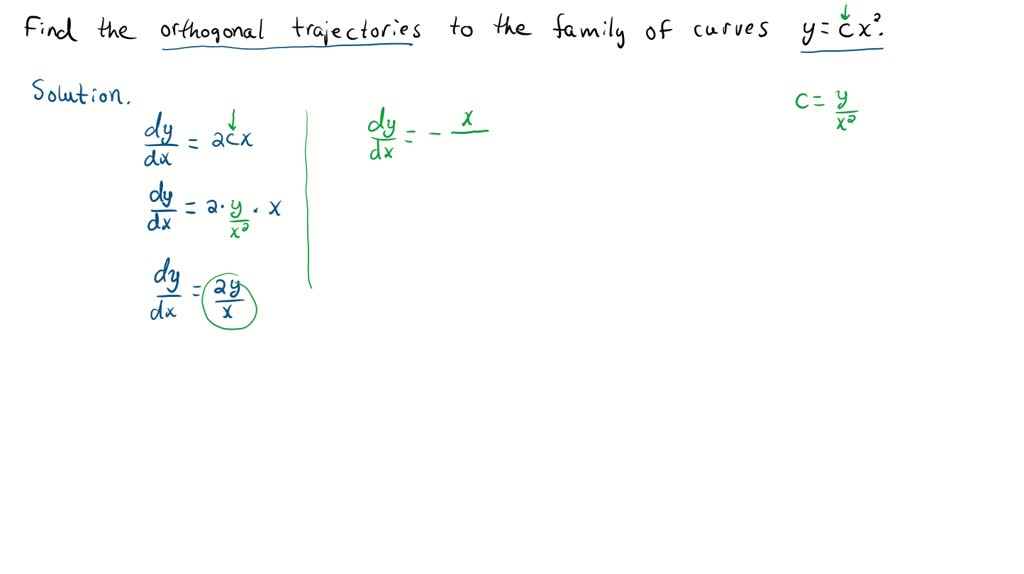
SOLVED:Find the equation of the orthogonal trajectories to the given family of curves. In each case, sketch some curves from each family. y=c x^2








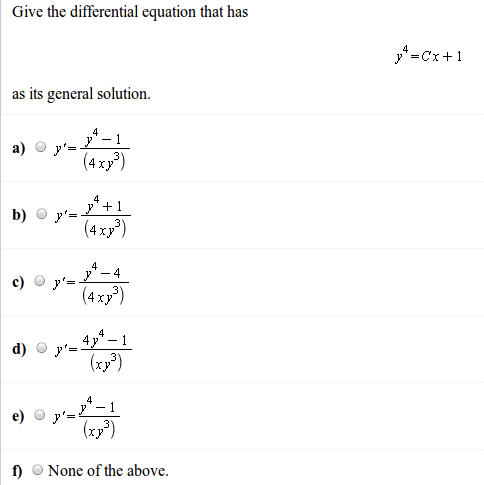

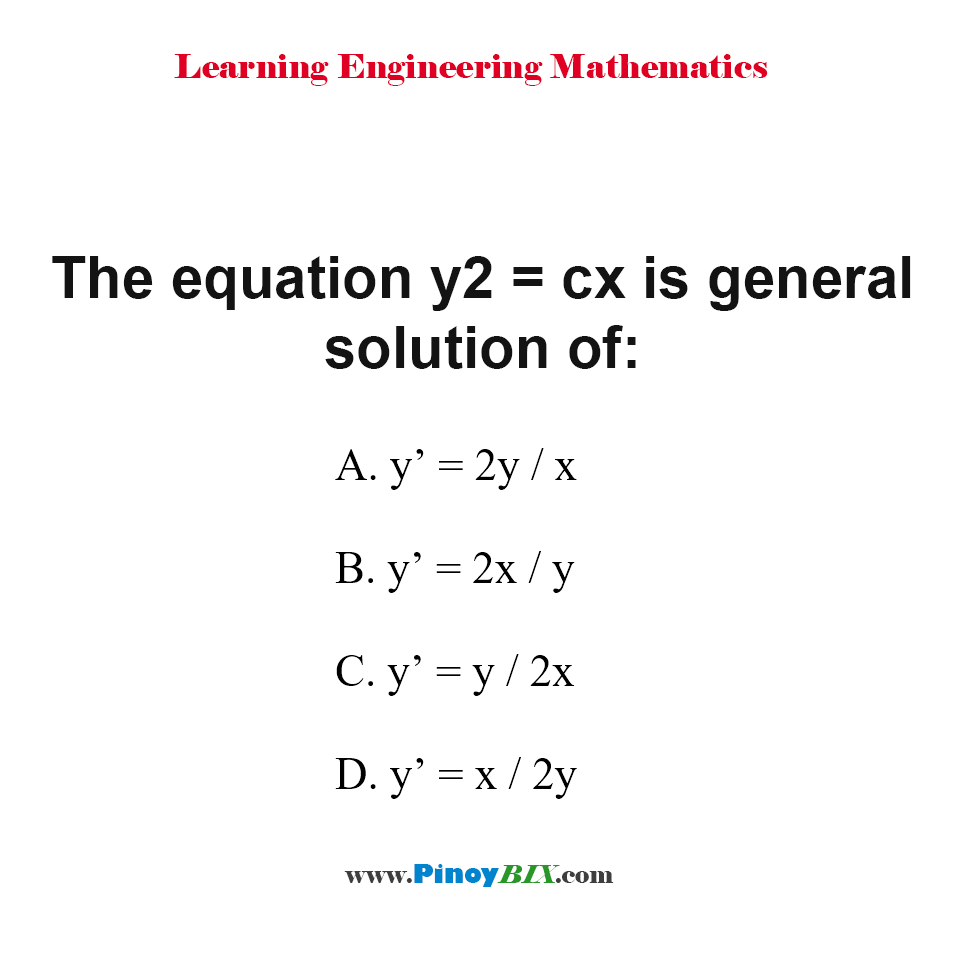
![MCQ] The general solution of differential equation y dx - x dy = 0 is MCQ] The general solution of differential equation y dx - x dy = 0 is](https://d1avenlh0i1xmr.cloudfront.net/599ab849-a797-4781-88aa-abedacdf4ae1/slide31.jpg)